Posted on: August 21, 2020 01:10 PM
Posted by: Renato
Views: 13303
A cheat sheet for Laravel’s Eloquent ORM version 5.5.
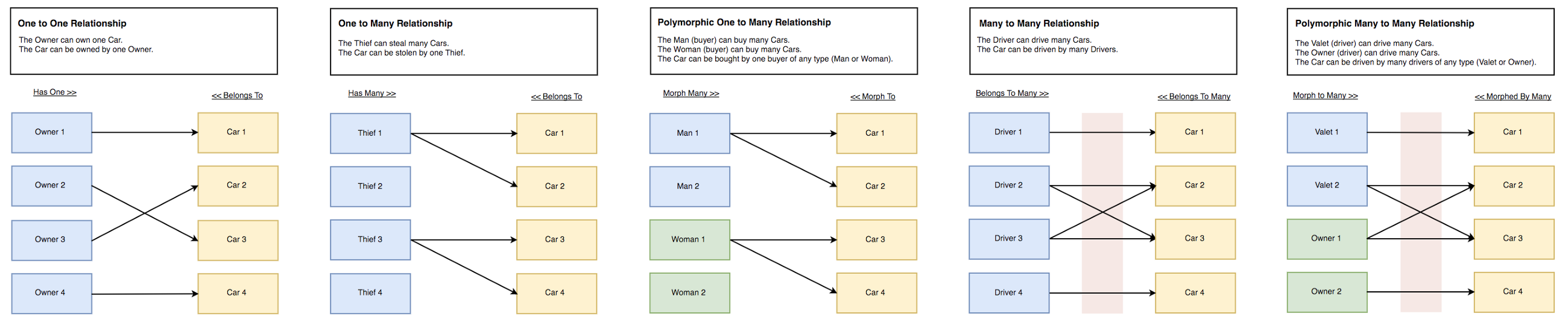
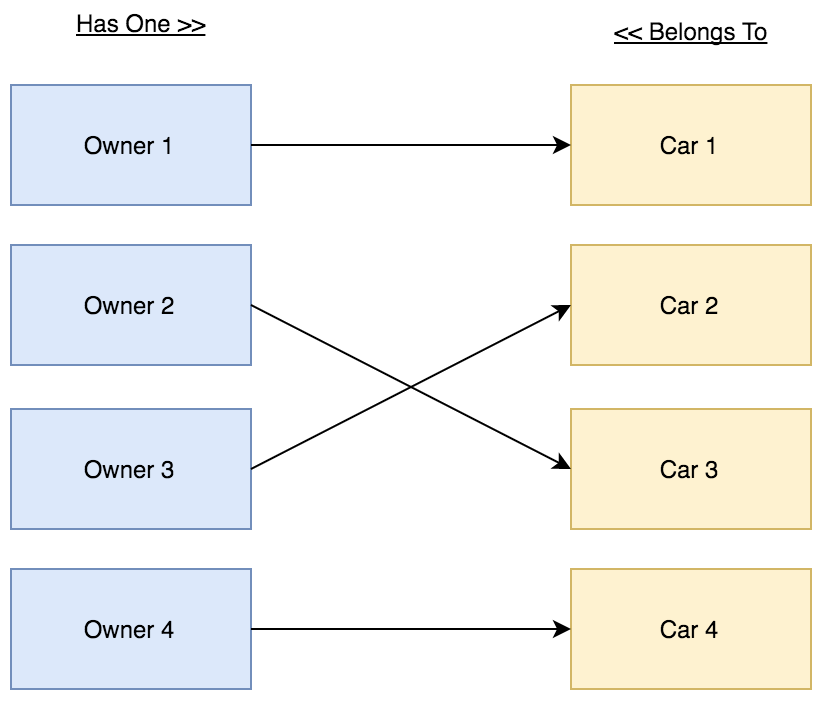
One to One Relationship
Demo details:
In this demo we have 2 models (Owner and Car), and 2 tables (owners and cars).
Business Rules:
The Owner can own one Car.
The Car can be owned by one Owner.
Relations Diagram:
Relationship Details:
The Cars table should store the Owner ID.
Eloquent Models:
class Owner
{
public function car()
{
return $this->hasOne(Car::class);
}
}
class Car
{
public function owner()
{
return $this->belongsTo(Owner::class);
}
}
Database Migrations:
Schema::create('owners', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('cars', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->integer('owner_id')->unsigned()->index()->nullable();
$table->foreign('owner_id')->references('id')->on('owners');
});
Store Records:
// Create relation between Owner and Car.
$owner->car()->save($car);
// Create relation between Car and Owner.
$car->owner()->associate($owner)->save();
Retrieve Records:
// Get Owner Car
$owner->car;
// Get Car Owner
$car->owner;
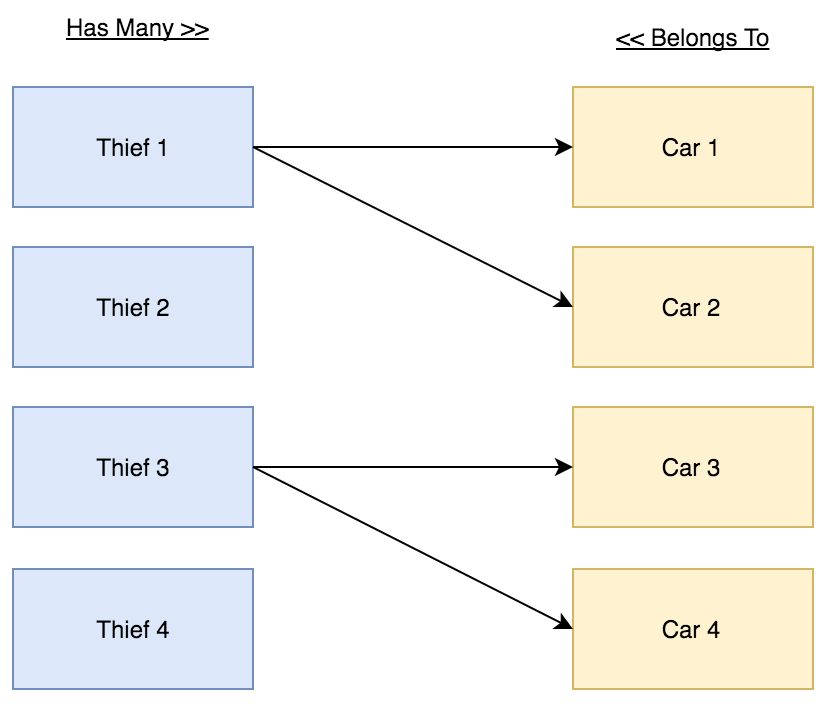
One to Many Relationship
Demo details:
In this demo we have 2 models (Thief and Car), and 2 tables (thieves and cars).
Business Rules:
The Thief can steal many Cars.
The Car can be stolen by one Thief.
Relations Diagram:
Relationship Details:
The Cars table should store the Thief ID.
Eloquent Models:
class Thief
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->hasMany(Car::class);
}
}
class Car
{
public function thief()
{
return $this->belongsTo(Thief::class);
}
}
Database Migrations:
Schema::create('thieves', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('cars', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->integer('thief_id')->unsigned()->index()->nullable();
$table->foreign('thief_id')->references('id')->on('thieves');
});
Store Records:
// Create relation between Thief and Car.
$thief->cars()->saveMany([ $car1, $car2, ]);
// Or use the save() function for single model.
$thief->cars()->save($car);
// Create relation between Car and Thief.
$car->thief()->associate($thief)->save();
Retrieve Records:
// Get Thief Car
$thief->cars;
// Get Car Thief
$car->thief;

Polymorphic One to Many Relationship
Demo details:
In this demo we have 3 models (Man, Woman and Car), and 3 tables (men, women and cars).
Business Rules:
The Man (buyer) can buy many Cars.
The Woman (buyer) can buy many Cars.
The Car can be bought by one buyer (Man or Woman).
Relations Diagram:
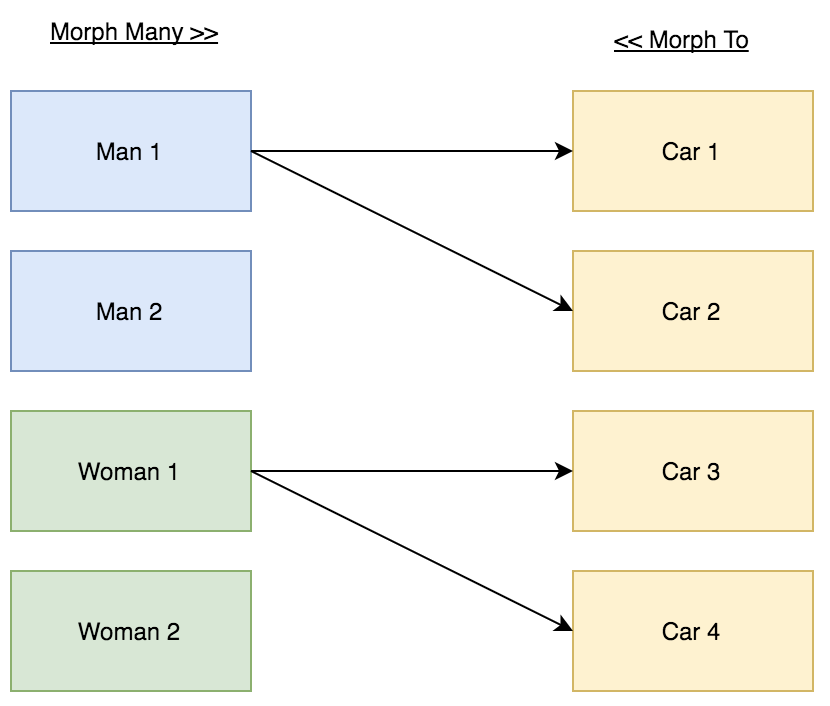
Relationship Details:
The Car table should store the Buyer ID and the Buyer Type.
“buyer” is a name given to a group of models (Man and Woman). And it’s not limited to two. The buyer type is the real name of the model.
Eloquent Models:
class Man
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->morphMany(Car::class, 'buyer');
}
}
class Woman
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->morphMany(Car::class, 'buyer');
}
}
class Car
{
public function buyer()
{
return $this->morphTo();
}
}
Database Migrations:
Schema::create('men', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('women', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('cars', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->integer('buyer_id')->unsigned()->index()->nullable();
$table->string('buyer_type')->nullable();
// or use $table->morphs(‘buyer’); instead of "buyer_id" and "buyer_type"
});
Store Records:
// Create relation between buyer (Man/Woman) and Car.
$man->cars()->saveMany([ $car1, $car2, ]);
$woman->cars()->saveMany([ $car1, $car2, ]);
// Or use the save() function for single model.
$man->cars()->save($car); $woman->cars()->save($car);
// Create relation between Car and buyer (Men/Women).
$car1->buyer()->associate($man)->save(); $car2->buyer()->associate($woman)->save();
Retrieve Records:
// Get buyer (Man/Woman) Cars
$men->cars $women->cars
// Get Car buyer (Man and Woman)
$car->buyer

Many to Many Relationship
Demo details:
In this demo we have 2 models (Driver and Car), and 3 tables (drivers, cars and a pivot table named car_driver).
Business Rules:
The Driver can drive many Cars.
The Car can be driven by many Drivers.
Relations Diagram:

Relationship Details:
The Pivot table “car_driver” should store the Driver ID and the Car ID.
Eloquent Models:
class Driver
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->belongsToMany(Car::class);
}
}
class Car
{
public function drivers()
{
return $this->belongsToMany(Driver::class);
}
}
Database Migrations:
Schema::create('drivers', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('cars', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('car_driver', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->integer('car_id')->unsigned()->index();
$table->foreign('car_id')->references('id')->on('cars')->onDelete('cascade');
$table->integer('driver_id')->unsigned()->index();
$table->foreign('driver_id')->references('id')->on('drivers')->onDelete('cascade');
});
Store Records:
// Create relation between Driver and Car.
$driver->cars()->attach([ $car1->id, $car2->id, ]);
// Or use the sync() function to prevent duplicated relations.
$driver->cars()->sync([ $car1->id, $car2->id, ]);
// Create relation between Car and Driver.
$car->drivers()->attach([ $driver1->id, $driver2->id, ]);
// Or use the sync() function to prevent duplicated relations.
$car->drivers()->sync([ $driver1->id, $driver2->id, ]);
Retrieve Records:
// Get Driver Car
$driver->cars
// Get Car Drivers
$car->drivers

Polymorphic Many to Many Relationship
Demo details:
In this demo we have 3 models (Valet, Owner and Car), and 4 tables (valets, owners, cars and drivers).
Business Rules:
The Valet (driver) can drive many Cars.
The Owner (driver) can drive many Cars.
The Car can be driven by many drivers (Valet or/and Owner).
Relations Diagram:

Relationship Details:
The Pivot table “drivers” should store the Driver ID, Driver Type and the Car ID.
“driver” is a name given to a group of models (Valet and Owner). And it’s not limited to two. The driver type is the real name of the model.
Eloquent Models:
class Valet
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->morphToMany(Car::class, 'driver');
}
}
class Owner
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->morphToMany(Car::class, 'driver');
}
}
class Car
{
public function valets()
{
return $this->morphedByMany(Valet::class, 'driver');
}
public function owners()
{
return $this->morphedByMany(Owner::class, 'driver');
}
}
Database Migrations:
Schema::create('valets', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('owners', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('drivers', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->integer('driver_id')->unsigned()->index();
$table->string('driver_type');
// or use $table->morphs(‘driver’); instead of "driver_id" and "driver_type"
$table->integer('car_id')->unsigned()->index();
$table->foreign('car_id')->references('id')->on('cars')->onDelete('cascade');
});
Store Records:
// Create relation between driver (Valet/Owner) and Car.
$valet->cars()->saveMany([$car1, $car2]); $owner->cars()->saveMany([$car1, $car2]);
// Or use the save() function for single model.
$valet->cars()->save($car1); $owner->cars()->save($car1);
// Create relation between Car and driver (Valet/Owner).
$car->valets()->attach([
$valet1->id,
$valet2->id,
]);
$car->owners()->attach([
$owner1->id,
$owner2->id,
]);
// Or use the sync() function to prevent duplicated relations.
$car->valets()->sync([
$valet1->id,
$valet2->id,
]);
$car->owners()->sync([
$owner1->id,
$owner2->id,
]);
Retrieve Records:
// Get driver (Valet/Owner) Cars
$valet->cars $owner->cars
// Get Car drivers (Valet and Owner)
$car->owners $car->valets

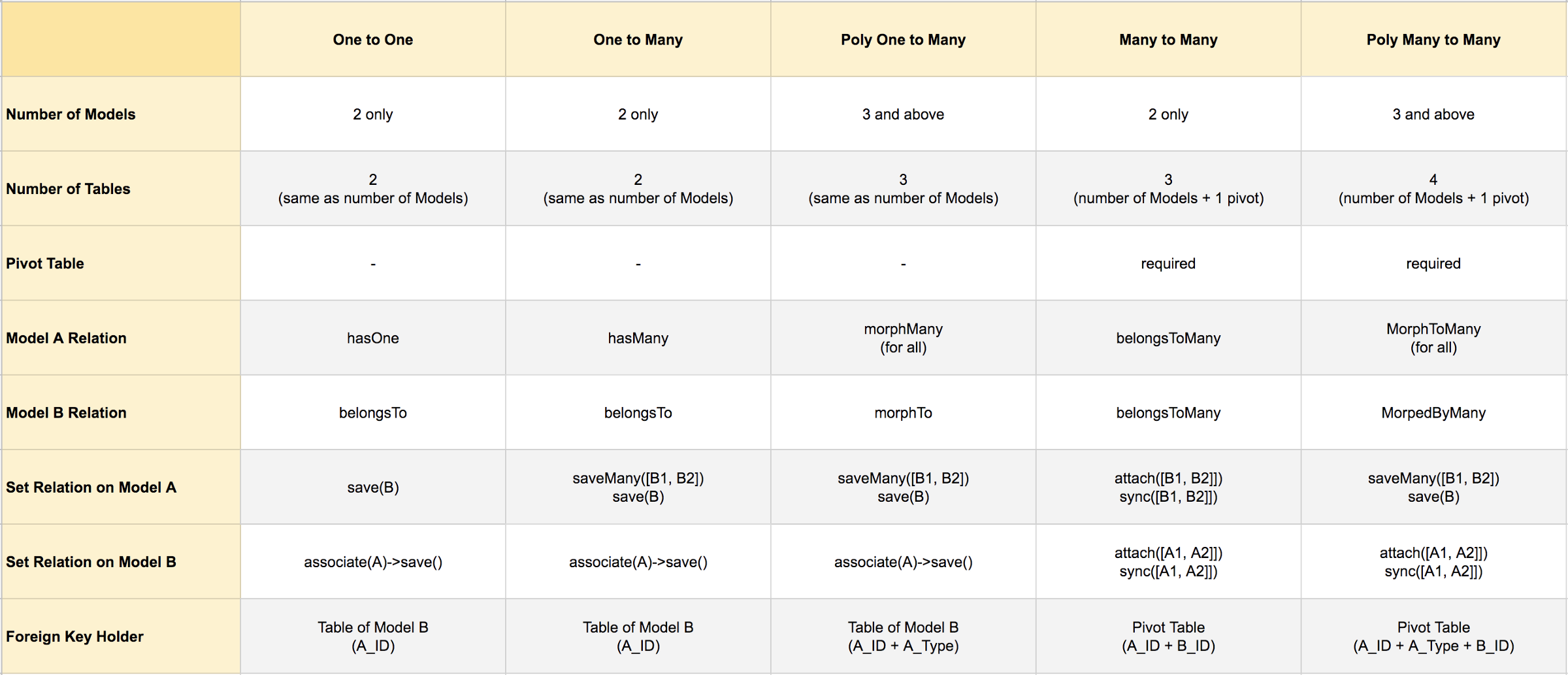
Fonte:
- https://hackernoon.com/eloquent-relationships-cheat-sheet-5155498c209
Donate to Site

Renato
Developer